| 导读 | tee用于读取标准输入的数据,将内容输出到屏幕,同时保存成文件,并且可以保存到多个文件。 |
如何使用tee
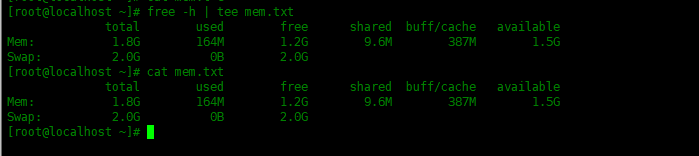
tee最基本的用法就是显示输出结果并且保存内容到文件中。下面例子使用free显示系统内存使用信息,并使用tee命令将信息输出到屏幕,并保存到文件mem.txt中。
[root@localhost ~]# free -h | tee mem.txt
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1.8G 164M 1.2G 9.6M 387M 1.5G
Swap: 2.0G 0B 2.0G
可以查看一下mem.txt文件,可以看到输出内容已经保存到mem.txt里面了。
写入到多个文件
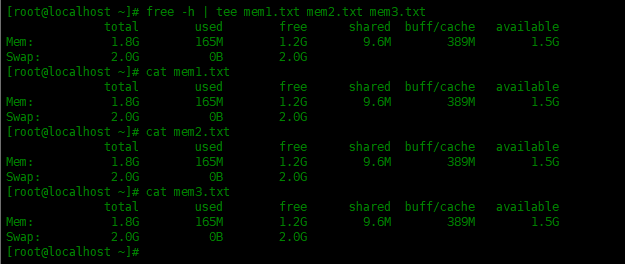
tee可以写入多个文件,每个文件之间使用空格分隔。
[root@localhost ~]# free -h | tee mem1.txt mem2.txt mem3.txt
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1.8G 165M 1.2G 9.6M 389M 1.5G
Swap: 2.0G 0B 2.0G
在已存在的文件底部追加内容
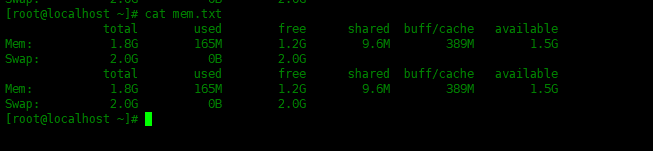
下面的例子使用选项-a在文件底部追加内容,不覆盖原有内容。
[root@localhost ~]# free -h | tee -a mem.txt
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1.8G 165M 1.2G 9.6M 389M 1.5G
Swap: 2.0G 0B 2.0G
可以看到,在mem.txt文件底部追加了新的内容。
如果不想在屏幕输出内容,可以使用>标准输出符号,重定向到/dev/null中:
[root@localhost ~]# free -h | tee -a mem.txt > /dev/null
总结
tee命令用于读取标准输入的数据,将内容输出到屏幕,同时保存成文件,并且可以保存到多个文件。
本文原创地址://gulass.cn/linux-tee-example.html编辑:倪家兴,审核员:逄增宝








